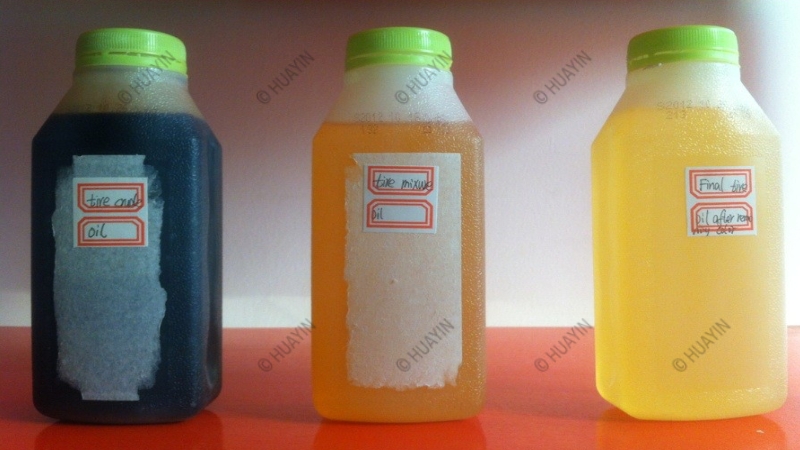
Tire pyrolysis oil is a type of pyrolysis oil that is produced by heating waste tires in the absence of oxygen through a process called tire pyrolysis.
This is a thermochemical decomposition process that converts the rubber and other organic compounds in the tires to decompose into liquid oil. The process of tire pyrolysis involves heating shredded or whole waste tires in a reactor to temperatures between 400 and 600°C in the absence of oxygen. The heat breaks down the rubber and other organic compounds in the tires into a liquid oil that can be used as fuel. Tire pyrolysis oil is a dark brown, viscous liquid that contains a mixture of organic compounds, including hydrocarbons, oxygenated compounds, and nitrogen-containing compounds. It has a high energy content and can be used as a fuel in boilers, furnaces for heating, and other industrial applications or electricity generation, as well as a feedstock for the production of chemicals. Tire pyrolysis oil has similar properties to other types of pyrolysis oil, including a high energy density and a mixture of organic compounds such as hydrocarbons, oxygenated compounds, and nitrogen-containing compounds. Additionally, the quality and composition of tire pyrolysis oil can vary depending on the type of tire being processed, the conditions of the pyrolysis process, and other factors. As a result, additional processing may be required to upgrade tire pyrolysis oil before it can be used as a transportation fuel.