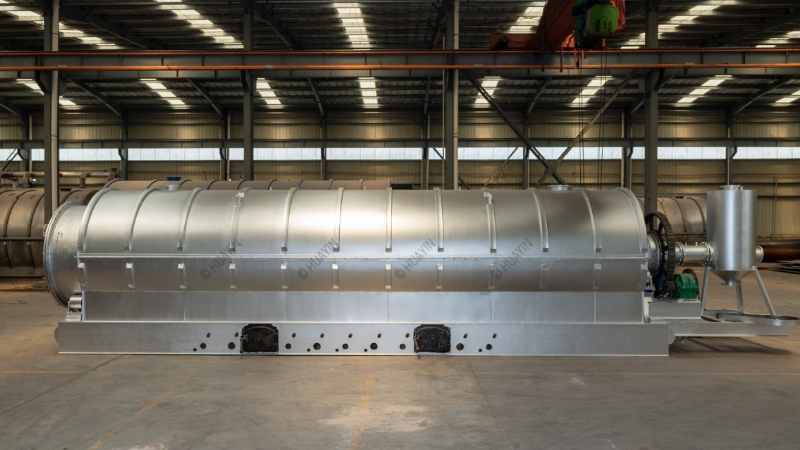
Waste tire pyrolysis is an effective resource recovery technology that can convert waste tires into useful fuels. Heating is a crucial step in this process, as it helps to decompose wastes into usable products. There are two common heating methods, direct heating and indirect heating.
Direct heating refers to exposing waste tires directly to high temperatures to decompose and convert them into oil and gas. The equipment commonly used for this heating method is a furnace. The waste tire is placed in a furnace and then heated to a high temperature. During this process, the waste tire undergoes pyrolysis reactions, producing oil and gas. Then the oil can be collected and extracted through condensation and separation. The direct heating pyrolysis plant is easy to operate, has fast heating speed, and is suitable for large-scale production. However, the exhaust gas and waste residue generated during the combustion process need to be treated to avoid environmental pollution.
Indirect heating refers to the transfer of heat to waste tires through conduction or convection to heat them up. The equipment commonly used for this heating method is hot air heating or heater. In the indirect heating process, waste tires are not directly exposed to high temperatures, but rather receive heat through the surface of the heater or the conductive medium. This heating method can reduce the waste gas and slag generated during the combustion process, thereby reducing the impact on the environment. In addition, indirect heating can better control the temperature and time of the heating process to obtain higher-quality products. However, indirect heating has a slow heating speed, relatively complex operation, and the need for more energy.
When selecting the heating method, it is necessary to consider factors such as production scale, operational requirements, and environmental impact to choose the most suitable heating method. Huayin provides customized designs and solutions for you to dispose of waste, contact us if you need to learn more details!