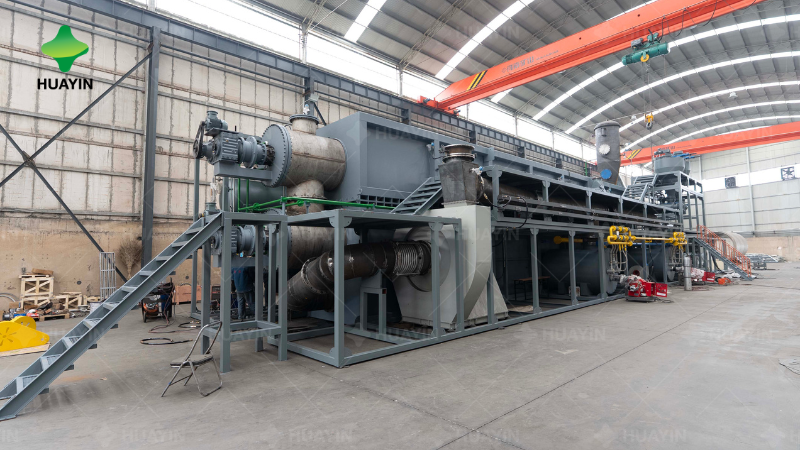
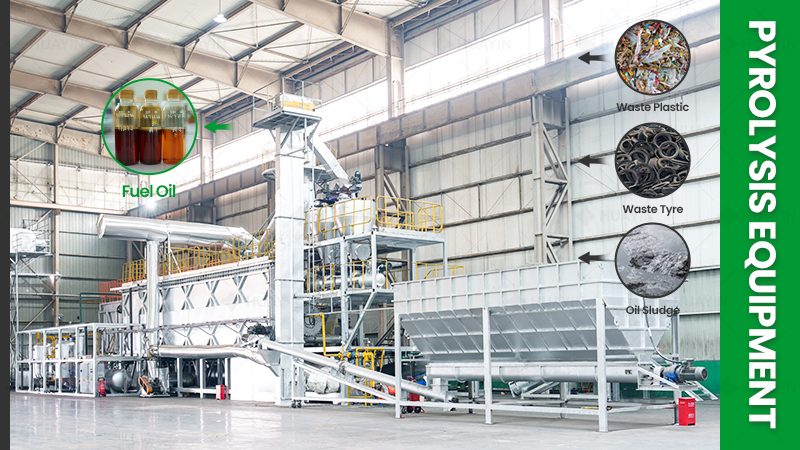
Among numerous waste treatment technologies, “pyrolysis” and “incineration” are two frequently mentioned methods. Although both involve high-temperature processing, their principles, purposes, and products are fundamentally different. Understanding the essential differences between these two technologies is crucial for selecting the most suitable solution for waste valorization or harmless disposal.

Pyrolysis Technology
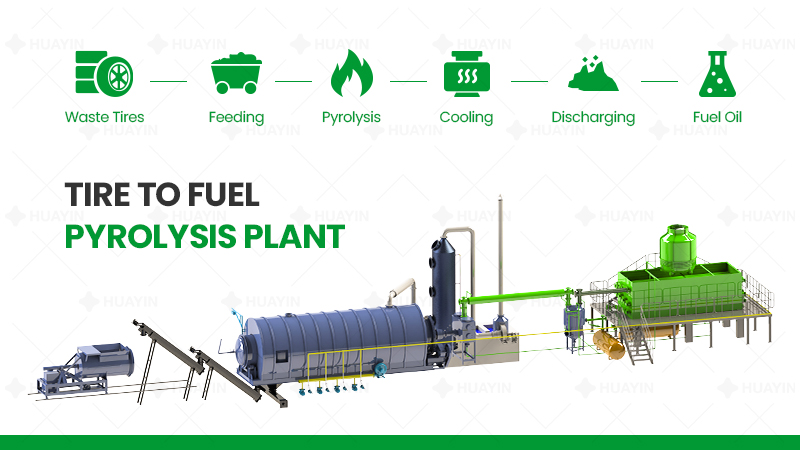
Pyrolysis is a process in which organic materials (such as plastics, rubber, biomass, etc.) undergo thermal decomposition at high temperatures (typically 300-800°C) in an oxygen-free or oxygen-deficient. Unlike direct combustion, pyrolysis does not completely burn the materials but converts them into various valuable products, achieving waste valorization and energy recovery.
The main products of pyrolysis include:
Pyrolysis Oil: A liquid fuel that can be used as industrial fuel or further refined into diesel, etc.
Carbon Black: A solid product that can be used in rubber, plastics, and other industrial fields.
Syngas: A synthetic gas that can be recycled to provide energy for the pyrolysis process or used for power generation.
Incineration Technology
Incineration, on the other hand, is the process of completely or partially burning solid waste in an environment with sufficient oxygen, with the final products being flue gas and ash. Modern incineration facilities often integrate “waste-to-energy” technology, utilizing the heat generated from combustion for power generation or heating, thereby achieving waste volume reduction and energy recovery.
The main purposes of incineration technology:
Waste Volume Reduction: High-temperature combustion significantly reduces the volume and weight of waste, effectively addressing the problem of insufficient landfill space.
Harmless Treatment: Particularly suitable for treating waste that is difficult to recycle or contains toxic and harmful substances, such as medical waste and some municipal solid waste, ensuring its safe disposal.
Energy Recovery: Utilizing the heat generated from combustion for power generation or heating, achieving energy reuse.
Unique Advantages of Pyrolysis over Incineration
Although incineration still holds an important position in waste treatment, pyrolysis technology is gaining increasing attention due to its unique advantages:
High Added Value Products: Pyrolysis products (such as pyrolysis oil and carbon black) have higher market value, which can bring more considerable economic returns to waste treatment.
Stronger Environmental Friendliness: The types and quantities of pollutants generated during the pyrolysis process are relatively fewer, especially in terms of harmful gas emissions, demonstrating significant environmental advantages.
Flexibility and Adaptability: Pyrolysis technology has broader adaptability to waste raw materials, capable of treating various complex organic waste components, and its products are diverse, facilitating subsequent utilization.

Pyrolysis and incineration are two waste treatment technologies, each with its own focus and complementary roles. Incineration still plays an irreplaceable role in achieving rapid waste volume reduction and harmless disposal, especially for large quantities of municipal solid waste and medical waste. Pyrolysis, on the other hand, shows great potential in waste valorization and high-value product recovery, serving as an important pathway for achieving a circular economy and sustainable development.



